Diverticular Disease and Diverticulitis
Diverticular disease and diverticulitis are related digestive conditions that affect the large intestine (bowel).
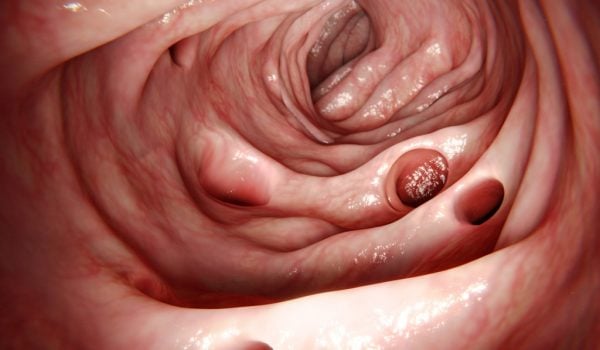
Diverticula are small bulges that can develop in the lining of the intestine as you get older.
When diverticula cause symptoms such as pain in the lower tummy, it’s called diverticular disease.
If the diverticula become inflamed or infected which causes more severe symptoms, it’s called diverticulitis.
You’re more likely to get diverticular disease and diverticulitis if you don’t have enough fibre in your diet.
What are the symptoms?
- Tummy pain usually in your lower left side, that tends to come and go and gets worse during or shortly after eating (emptying your bowels or passing wind eases it)
- Feeling bloated
- Constipation, diarrhoea or both
- Occasionally, mucus in your stool
If your diverticula become infected and inflamed (diverticulitis), you may suddenly.
- Get constant, more severe tummy pain
- Have a high temperature of 38C or above
- Feel sick or vomit
- Feel generally tired and unwell
- Get blood in your stool or bleeding from your bottom (rectal bleeding)
Treatment options
In serious cases, surgery may be needed to treat serious complications of diverticulitis.
Surgery usually involves removing the affected section of your large intestine. This is known as a colectomy.
This is the treatment for rare complications such as fistulas, peritonitis or a blockage in your intestines.
After a colectomy, you may have a temporary or permanent colostomy, where one end of your bowel is diverted through an opening in your tummy.
The most common complication of diverticulitis is developing abscesses.
These are usually treated with a technique known as percutaneous drainage or a laparoscopic washout which is done by a radiologist.
